
jaffle_shop is a fictional ecommerce store. This dbt project transforms raw data from an app database into a customers and orders model ready for analytics.
This repo contains seeds that includes some (fake) raw data from a fictional app.
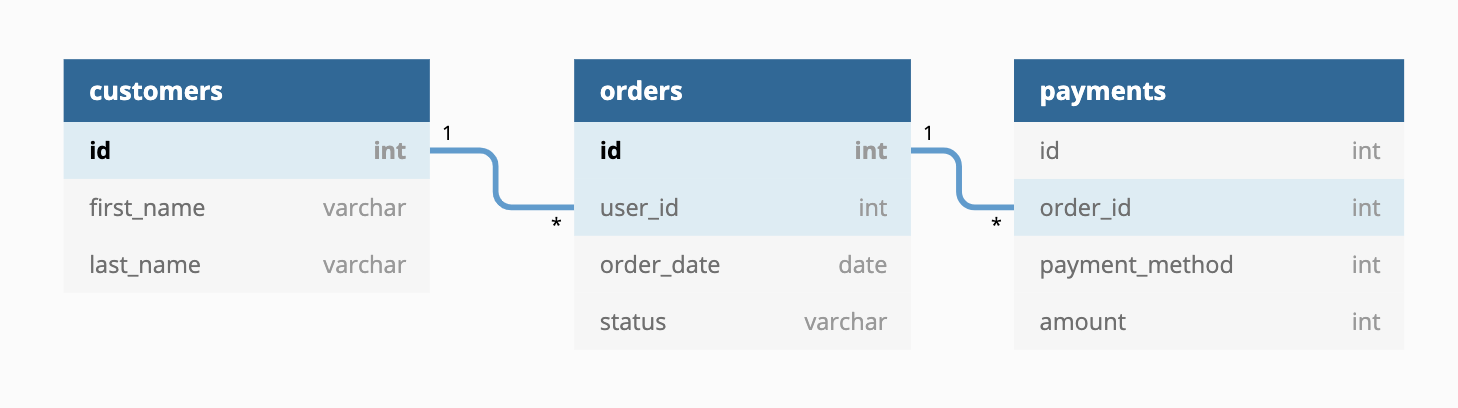
The raw data consists of customers, orders, and payments, with the following entity-relationship diagram:
To get up and running with this project:
Note : Before running this commands first give command of ” venv/Scripts/activate ” to acticate the environment.
-
Install dbt using these instructions.
-
Clone this repository.
-
Change into the
jaffle_shopdirectory from the command line:
$ cd jaffle_shop-
Set up a profile called
jaffle_shopto connect to a data warehouse by following these instructions. If you have access to a data warehouse, you can use those credentials – we recommend setting your target schema to be a new schema (dbt will create the schema for you, as long as you have the right privileges). If you don’t have access to an existing data warehouse, you can also setup a local postgres database and connect to it in your profile. -
Ensure your profile is setup correctly from the command line:
$ dbt debug- Load the CSVs with the demo data set. This materializes the CSVs as tables in your target schema. Note that a typical dbt project does not require this step since dbt assumes your raw data is already in your warehouse.
$ dbt seed- Run the models:
$ dbt runNOTE: If this steps fails, it might mean that you need to make small changes to the SQL in the models folder to adjust for the flavor of SQL of your target database. Definitely consider this if you are using a community-contributed adapter.
- Test the output of the models:
$ dbt test- Generate documentation for the project:
$ dbt docs generate- View the documentation for the project:
$ dbt docs serveA jaffle is a toasted sandwich with crimped, sealed edges. Invented in Bondi in 1949, the humble jaffle is an Australian classic. The sealed edges allow jaffle-eaters to enjoy liquid fillings inside the sandwich, which reach temperatures close to the core of the earth during cooking. Often consumed at home after a night out, the most classic filling is tinned spaghetti, while my personal favourite is leftover beef stew with melted cheese.
For more information on dbt:
- Read the introduction to dbt.
- Read the dbt viewpoint.
- Join the dbt community.
 https://github.com/KunjPathak12/myJaffleShop-DBT
https://github.com/KunjPathak12/myJaffleShop-DBT